Publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2026
- Review
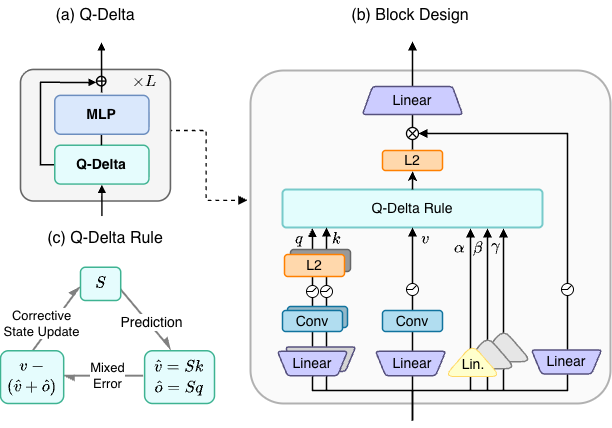 Q-Delta: Beyond Key–Value Associative State EvolutionSumin Park, Seojin Kim, and Noseong ParkIn Review, 2026
Q-Delta: Beyond Key–Value Associative State EvolutionSumin Park, Seojin Kim, and Noseong ParkIn Review, 2026Linear attention reformulates sequence modeling as recurrent state evolution, enabling efficient linear-time inference. Under the key–value associative paradigm, existing approaches restrict the role of the query to the readout operation, decoupling it from state evolution. We show that query-conditioned state readout induces a structured value prediction over accumulated memory that complements key-based retrieval. Based on this insight, we propose Q-Delta, a query-aware delta rule that integrates mixed key–query prediction errors into state evolution, enabling jointly corrective dynamics while preserving delta-rule efficiency. We establish stability guarantees for the resulting dynamics and derive a hardware-efficient chunkwise-parallel formulation with a custom Triton implementation. Empirical results demonstrate stable optimization, competitive throughput, and consistent improvements over strong baselines on language modeling and long-context retrieval tasks.
- Review
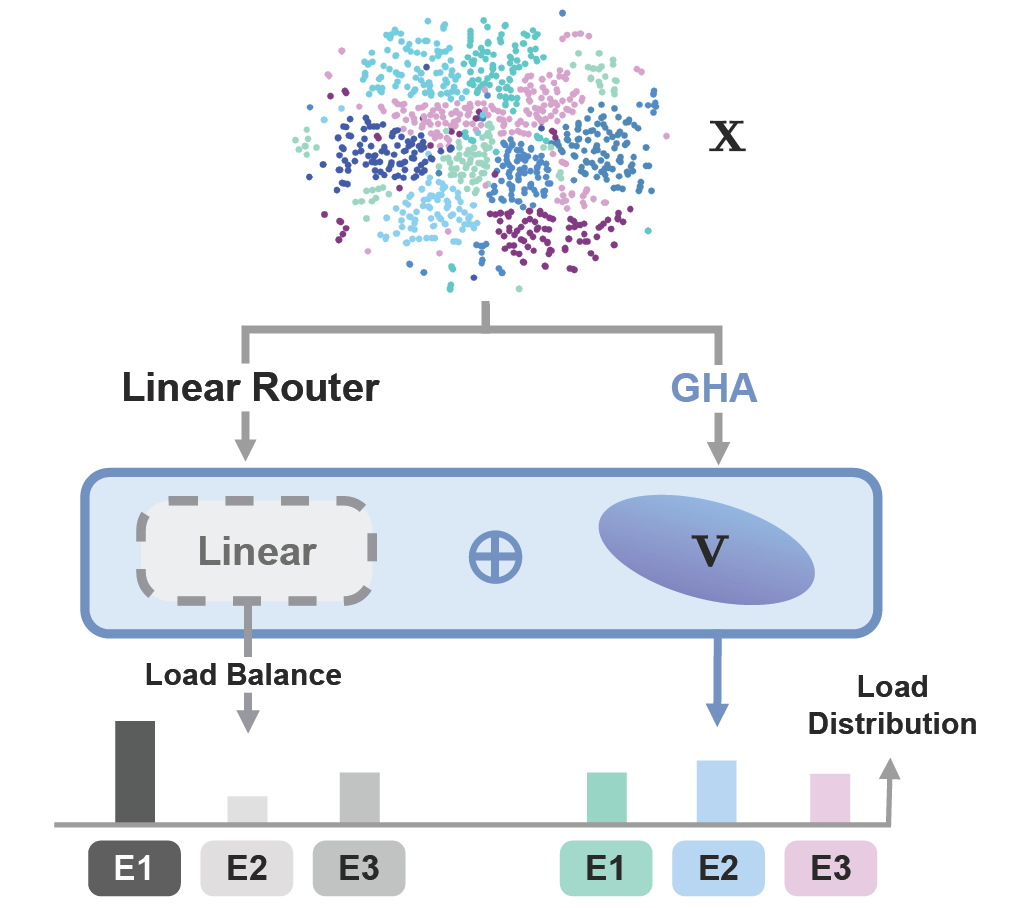 STAR: Rethinking MoE Routing as Structure-Aware Subspace LearningSumin Park and Noseong ParkIn Review, 2026
STAR: Rethinking MoE Routing as Structure-Aware Subspace LearningSumin Park and Noseong ParkIn Review, 2026Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) scales model capacity efficiently by selectively routing inputs to a specialized subset of experts. However, input-expert specialization, the core motivation of MoE, critically depends on whether the router is actually aware of input structure. In practice, MoE routing is typically implemented as a shallow linear projection with limited awareness of input representation, which often leads to unstable and suboptimal specialization. We propose STAR, a STructure-Aware Routing that rethinks MoE routing as a subspace learning problem by augmenting standard learnable routing with an evolving principal subspace that tracks dominant input structure via Generalized Hebbian Algorithm (GHA). By aligning routing decisions directly with input structure along with the task-supervision from learnable gate, STAR enables stable and balanced expert specialization without relying on auxiliary load-balancing losses. We evaluate STAR on controlled synthetic setup and large-scale language and vision tasks, where it consistently improves routing quality and downstream performance over strong MoE baselines. Moreover, optional testtime subspace updates further enhance routing robustness under distribution shifts.
2025
- AAAI
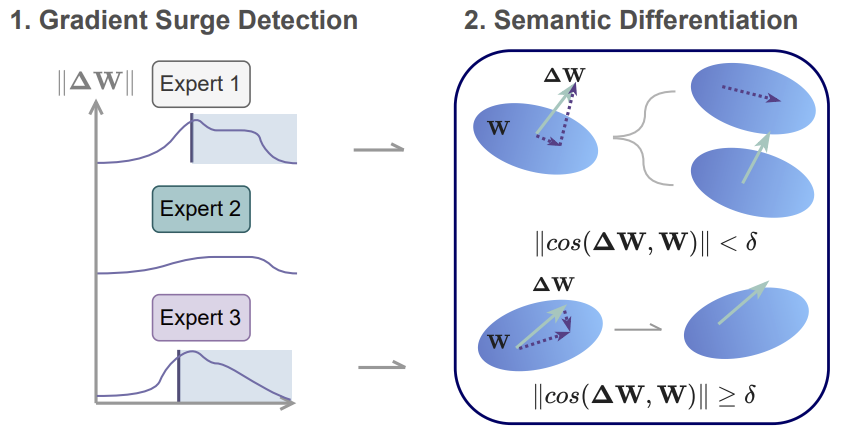 How Many Experts Are Enough? Towards Optimal Semantic Specialization for Mixture-of-ExpertsSumin Park and Noseong ParkIn Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2025
How Many Experts Are Enough? Towards Optimal Semantic Specialization for Mixture-of-ExpertsSumin Park and Noseong ParkIn Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2025Finding the optimal configuration of Sparse Mixture-ofExperts (SMoE) that maximizes semantic differentiation among experts is essential for exploiting the full potential of MoE architectures. However, existing SMoE frameworks either heavily rely on hyperparameter tuning or overlook the importance of diversifying semantic roles across experts when adapting the expert pool size. We propose Mixture-of-Experts for Adaptive Semantic Specialization (MASS), a semanticaware MoE framework for adaptive expert expansion and dynamic routing. MASS introduces two key advancements: (i) a gradient-based semantic drift detector that prompts targeted expert expansion when the existing expert pool lacks capacity to capture the full semantic diversity of the data, and (ii) an integration of adaptive routing strategy that dynamically adjusts expert usage based on token-level routing confidence mass. We first demonstrate that MASS reliably converges to the point of optimal balance between cost-performance trade-off with notably improved sematic specialization in a highly controlled synthetic setup. Further empirical results on real-world datasets across language and vision domains show that MASS consistently outperforms a range of strong MoE baselines, demonstrating its domain robustness and enhanced expert specialization.
2024
- ICML
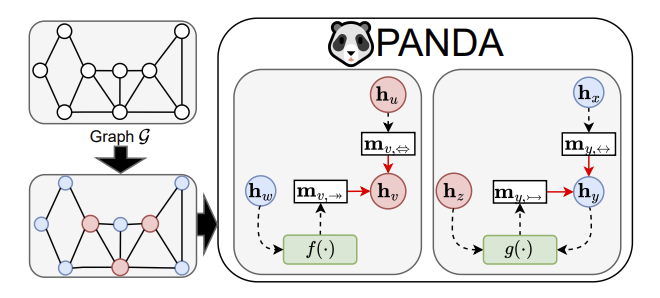 PANDA: Expanded Width-Aware Message Passing Beyond RewiringJeongwhan Choi, Sumin Park, Hyowon Wi, and 2 more authorsIn International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2024
PANDA: Expanded Width-Aware Message Passing Beyond RewiringJeongwhan Choi, Sumin Park, Hyowon Wi, and 2 more authorsIn International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2024Recent research in the field of graph neural network (GNN) has identified a critical issue known as "over-squashing," resulting from the bottleneck phenomenon in graph structures, which impedes the propagation of long-range information. Prior works have proposed a variety of graph rewiring concepts that aim at optimizing the spatial or spectral properties of graphs to promote the signal propagation. However, such approaches inevitably deteriorate the original graph topology, which may lead to a distortion of information flow. To address this, we introduce an expanded width-aware (PANDA) message passing, a new message passing paradigm where nodes with high centrality, a potential source of over-squashing, are selectively expanded in width to encapsulate the growing influx of signals from distant nodes. Experimental results show that our method outperforms existing rewiring methods, suggesting that selectively expanding the hidden state of nodes can be a compelling alternative to graph rewiring for addressing the over-squashing.
- ICLR Workshop
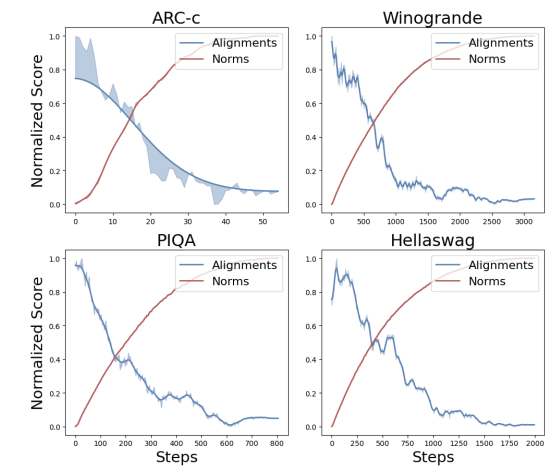 DARS: ROBUST SPARSE FINE-TUNING WITH REGULARIZED SUBSPACE DISALIGNMENTSumin Park and Noseong ParkIn First Workshop on Scalable Optimization for Efficient and Adaptive Foundation Models (SCOPE), 2024
DARS: ROBUST SPARSE FINE-TUNING WITH REGULARIZED SUBSPACE DISALIGNMENTSumin Park and Noseong ParkIn First Workshop on Scalable Optimization for Efficient and Adaptive Foundation Models (SCOPE), 2024Recent works have identified the alignment, which measures a layerwise weight correlation, as a novel yet crucial mechanism for feature learning. We investigate an underlying connection between the alignment learning and the structural fitting of a network to the training data span. Based on this insight, we further demonstrate that fine-tuning on out-of-distribution (OOD) data disrupts this well-aligned structure fitted during the pre-training phase, degrading generalization performance. To address this, we propose DARS, DisAlignment-Regularized Sparse fine-tuning, a novel sparse fine-tuning approach that mitigates disalignment by letting the gradient update to be partially constrained within the principal subspace of the pre-trained network, constructed based on the in-distribution (ID) data used for its pre-training. Specifically, we define the two disjoint subsets of trainable parameters for sparse channel unfreezing: i) a random subset and ii) a subset with higher gradient projections onto the principal subspace. The latter serves as a disalignment regularizer during fine-tuning, while the random subset ensures a minimal bias in parameter selection. By adjusting the ratio between the two subsets, we can control the strength of subspace regularization, thereby balancing the trade-off between generalization capacity and strong fitting to new downstream tasks. By employing DARS, we achieved SOTA performance on various benchmarks, including commonsense and arithmetic reasoning tasks, across LLaMA-7B and LLaMA2-7B.